
Part 1: Cyber Security Asliyat Mein Kya Hai?
Swagat hai aapka Cyber Security ki duniya mein. Shuru karne se pehle, ek galatfehmi door karte hain.
Zyada tar log sochte hain ki Cyber Security ka matlab hai—"Hacker ko rokna". Lekin ye adhoora sach hai.
Cyber Security ka asli matlab hai—"Data (Jaankari) ki suraksha karna".
Aaj ke zamane mein, Data hi naya Oil hai. Aapka bank balance, aapki chats, aapki photos, aur aapki location—sab
kuch data hai. Agar ye data internet par hai, to ye jokhim (risk) mein hai. Cyber Security wo process, technology
aur mindset hai jisse hum is data ko unauthorized access se bachate hain.
Why Cyber Security Matters: Real Numbers
Statistics se samjhte hain ki ye kitna zaroori hai:
- 2023 Data: Har 39 seconds mein ek cyber attack hota hai.
- Cost: Average data breach ki cost $4.45 million hai (2023).
- India: 2023 mein India mein 1.3 million cyber attacks report hue.
- Ransomware: 2023 mein ransomware attacks 41% badh gaye.
- Global Impact: 2024 tak, cybercrime ki total cost $10.5 trillion annually ho gayi hai.
- Small Businesses: 43% cyber attacks small businesses par target hote hain—kyunki unke paas security budget kam hota hai.
- Phishing: 91% successful cyber attacks phishing se start hote hain.
- Time to Detect: Average breach detect hone mein 207 days lagte hain—ye bahut zyada hai.
- IoT Devices: 2024 mein 75 billion IoT devices connected honge—har device ek potential entry point hai.
- Cloud Attacks: 2023 mein cloud-based attacks 95% badh gaye—kyunki companies cloud migrate kar rahi hain.
Types of Cyber Security
Cyber Security ko categories mein divide kiya ja sakta hai. Har category ka apna specific role hai:
1. Network Security
Focus: Network ko protect karna—firewalls, VPNs, intrusion detection systems.
Tools: Wireshark, Nmap, Firewall rules, IDS/IPS systems.
Example: Company ke internal network ko external attacks se bachana.
2. Application Security
Focus: Software aur apps ko secure karna—code reviews, penetration testing.
Tools: Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, SonarQube, SAST/DAST tools.
Example: Web application mein SQL injection vulnerabilities find karna aur fix karna.
3. Information Security
Focus: Data ko protect karna—encryption, access controls, data loss prevention.
Tools: Encryption software, DLP solutions, Data classification tools.
Example: Customer data ko encrypt karke store karna, aur sirf authorized users ko access
dena.
4. Operational Security
Focus: Processes aur procedures—backup plans, incident response, disaster recovery.
Tools: Backup systems, SIEM, Incident response platforms.
Example: Attack hone par kaise respond karna, backup se data restore karna.
5. Endpoint Security
Focus: Devices ko protect karna—antivirus, device encryption, mobile device management.
Tools: Antivirus, EDR (Endpoint Detection & Response), MDM solutions.
Example: Employee laptops par antivirus install karna, mobile devices ko manage karna.
6. Cloud Security
Focus: Cloud services ko secure karna—AWS security, data encryption in cloud.
Tools: AWS Security Groups, Azure Security Center, CloudTrail.
Example: AWS S3 buckets ko public access se protect karna, cloud resources ko monitor
karna.
7. Mobile Security
Focus: Mobile devices aur apps ko secure karna—app security, device management.
Tools: Mobile Device Management (MDM), App security scanners.
Example: Company mobile apps mein security vulnerabilities check karna.
8. IoT Security
Focus: Internet of Things devices ko secure karna—smart cameras, routers, sensors.
Tools: Network segmentation, Device authentication, Firmware updates.
Example: Smart home devices ko secure network par isolate karna.
9. Identity & Access Management
Focus: Users ko identify karna aur access control—SSO, MFA, role-based access.
Tools: Active Directory, Okta, Azure AD, IAM platforms.
Example: Employees ko role ke basis par permissions dena—HR ko salary data, IT ko server
access.
Part 2: The Golden Rule - The CIA Triad
Duniya ka koi bhi security system—chahe wo Google ka ho, Indian Army ka, ya aapke ghar ke WiFi ka—wo sirf ek hi
model par kaam karta hai: The CIA Triad.
Agar hacker ko jeetna hai, to use in 3 pillars mein se kisi ek ko todna hoga. Aur agar humein jeetna hai, to
humein in teeno ko mazboot rakhna hoga.
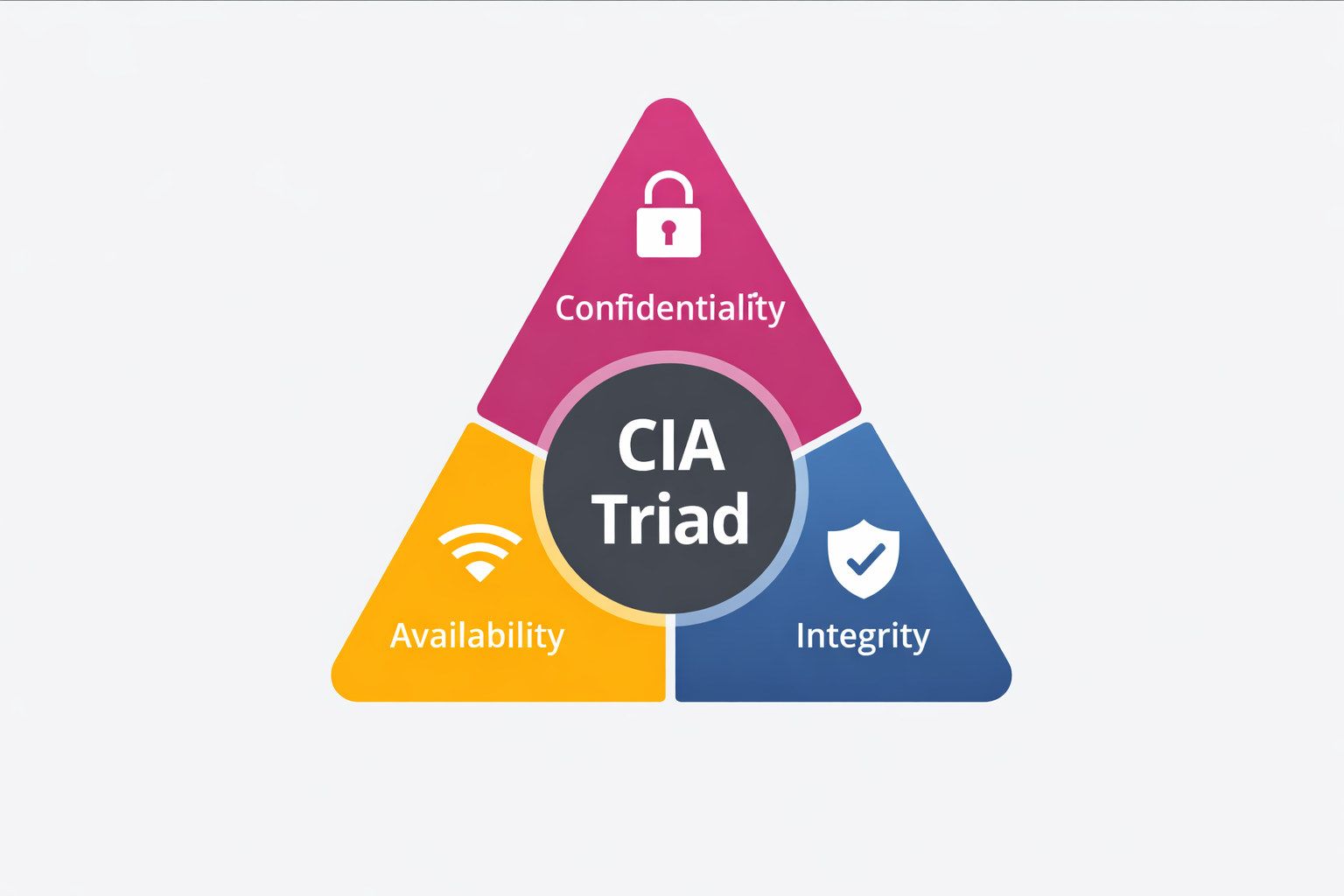
1. Confidentiality (Guptata)
Matlab: "Sirf wahi dekhe jise dekhna chahiye."
Imagine karein aapne Amazon se kuch order kiya. Aapne Credit Card details daali. Agar wo details Amazon ke
alawa kisi aur (hacker) ko dikh gayi, to Confidentiality fail ho gayi.
Kaise Todte Hain? Phishing, Man-in-the-Middle attack, Packet Sniffing, Eavesdropping, Social
Engineering.
Kaise Bachate Hain? Encryption (AES-256, RSA), Strong Passwords, 2FA/MFA, Access Control
Lists (ACL), Data Classification.
Real Example: 2017 Equifax breach mein 147 million Americans ka personal data leak hua—SSN,
credit card numbers. Ye confidentiality ka massive failure tha.
2. Integrity (Bharosa/Shuddhta)
Matlab: "Data badla na gaya ho."
Maan lijiye aapne apne dost ko ₹100 Google Pay kiye. Server tak jaate-jaate agar hacker ne us ₹100 ko ₹10000
kar diya, to data "corrupt" ho gaya. Yahan data chori nahi hua, bas badal gaya.
Kaise Todte Hain? Virus, Malware, SQL Injection, Man-in-the-Middle attacks, Unauthorized
modifications, Data tampering.
Kaise Bachate Hain? Hashing (SHA-256, MD5 checksums), Digital Signatures (RSA, DSA),
Version Control, Write-Once Storage, Checksums.
Real Example: 2015 Ukraine Power Grid attack mein hackers ne SCADA systems ko modify kiya,
jisse 230,000 people ko power cut hua. Ye integrity attack tha.
3. Availability (Uplabdhta)
Matlab: "Jab chahiye, tab mile."
Agar aapko Hospital mein admit hona hai aur computer system hi na chale, to wo security failure hai. Hacker
data churata nahi hai, bas system ko band kar deta hai.
Kaise Todte Hain? DDoS Attacks (Distributed Denial of Service), Ransomware, Physical attacks,
Natural disasters, Hardware failures, Network congestion.
Kaise Bachate Hain? Backups (3-2-1 rule), Redundant Servers (Load balancing), Failover
systems, Disaster Recovery Plans, CDN (Content Delivery Networks), Redundancy.
Real Example: 2016 Dyn DDoS attack ne Twitter, Netflix, Reddit ko down kar diya. Attackers ne
IoT devices (cameras, routers) ka use kiya—ye largest DDoS attack tha (1.2 Tbps).
CIA Triad in Real-World Scenarios
CIA Triad Trade-offs: Real Dilemmas
Real world mein, humesha teeno pillars perfect nahi ho sakte. Kuch trade-offs hote hain:
- High Confidentiality vs Availability: Agar aap data ko bahut secure rakhte hain (multiple encryption layers), to access slow ho sakta hai. Example: Banking apps secure hain, lekin thoda slow hote hain.
- High Integrity vs Performance: Har transaction ko verify karna (checksums, signatures) time leta hai. Example: Blockchain secure hai, lekin slow hai.
- High Availability vs Security: System ko always-on rakhte hain, to maintenance windows kam hote hain—patches install karna mushkil ho jata hai.
Part 3: The Jargon Buster (Hacker ki Bhasha)
Agar aapko Cyber Security expert banna hai, to aapko sahi shabd use karne aane chahiye. "Hack ho gaya" bolna beginner lagta hai. Aaiye professional terms seekhein.
-
Asset (Sampatti):
Koi bhi cheez jo valuable hai. (Ex: Aapka Laptop, User Data, Intellectual Property). -
Vulnerability (Kamzori/Loophole):
System mein koi chhed ya galti. (Ex: Windows update nahi kiya, ya kamzor password "123456" rakha). -
Threat (Khatra):
Koi bhi jo us kamzori ka fayda utha sakta hai. (Ex: Hacker, Virus, ya aag lagna). -
Exploit (Hathiyar):
Wo code ya technique jisse vulnerability ka use kiya jaye. (Ex: Metasploit tool).
Agar Vulnerability (Kamzori) hai lekin koi Threat (Hacker) nahi hai, to Risk kam hai.
Lekin Vulnerability + Threat = Risk (High Danger).
Risk Calculation: Risk = Threat × Vulnerability × Impact
Example: High Threat (Expert Hacker) × High Vulnerability (No Firewall) × High Impact (Bank Data) = CRITICAL RISK
More Security Terms - Complete Glossary
-
Zero-Day Vulnerability:
Wo vulnerability jo abhi tak discover nahi hui hai. Developer ko bhi nahi pata. Ye sabse dangerous hoti hai kyunki koi patch nahi hota.
Example: Stuxnet worm ne zero-day exploit use kiya Iran ke nuclear facilities ko attack karne ke liye. -
Penetration Testing (Pen Testing):
Authorized hacking—security experts ko permission dete hain system hack karne ki taaki weaknesses find kar sakein.
Types: Black Box (no knowledge), White Box (full knowledge), Gray Box (partial knowledge). -
SOC (Security Operations Center):
Ek dedicated team jo 24/7 systems monitor karti hai aur threats detect karti hai.
Real Example: Microsoft ka SOC har din 6.5 trillion security signals process karta hai. -
SIEM (Security Information and Event
Management):
Software jo logs collect karta hai aur suspicious activities detect karta hai.
Popular Tools: Splunk, IBM QRadar, ArcSight, LogRhythm. -
APT (Advanced Persistent Threat):
Long-term, sophisticated attack jisme attacker months/years tak system mein rehta hai, slowly data steal karta hai.
Example: APT28 (Fancy Bear) - Russian group jo 2007 se active hai, government targets attack karta hai. -
Malware:
Malicious software—virus, trojan, worm, ransomware, spyware sab malware ke types hain.
Types: Virus (self-replicating), Trojan (disguised), Worm (network spread), Ransomware (locks data). -
Firewall:
Network security device jo traffic ko filter karta hai—allowed/blocked decide karta hai.
Types: Network Firewall (hardware), Host Firewall (software), Next-Gen Firewall (deep inspection). -
IDS/IPS:
Intrusion Detection System (detect karta hai) vs Intrusion Prevention System (detect + block karta hai).
Difference: IDS sirf alert deta hai, IPS automatically block kar deta hai suspicious traffic ko. -
Sandbox:
Isolated environment jahan suspicious files ko safely test kiya ja sakta hai.
Use Case: Unknown email attachment ko sandbox mein open karke check karna ki malware hai ya nahi. -
Honeypot:
Fake system jo attackers ko attract karta hai—real systems ko protect karne ke liye.
Example: Fake database server jo attackers ko dikhaye, lekin real data nahi hai—attacker ko track karne ke liye. -
Threat Intelligence:
Information about current aur emerging threats—attackers ke methods, tools, targets.
Sources: Dark web monitoring, security feeds, threat sharing platforms (MISP, STIX/TAXII). -
Red Team vs Blue Team:
Red Team = Attackers (pen testers), Blue Team = Defenders (SOC analysts). Purple Team = Dono ko combine karke practice.
Purpose: Red team attacks simulate karta hai, Blue team defend karta hai—training ke liye.
Part 4: The AAA Model
CIA ke baad sabse zaroori concept hai AAA. Ye tay karta hai ki system ke andar kaun aayega aur kya kar sakta hai.
1. Authentication (Pehchan)
Ye check karta hai ki aap Kaun hain?
Ex: Password, Fingerprint, Face ID, OTP, Biometric.
Types:
• Something you know (Password, PIN)
• Something you have (Smart Card, Token)
• Something you are (Biometric - Fingerprint, Iris)
MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication): Jab 2 ya zyada methods combine hote hain—password + OTP =
Strong Security
2. Authorization (Adhikar)
Aapko kya karne ki Permission hai?
Ex: Student result dekh sakta hai (Read), lekin Teacher result badal sakta hai (Write).
Access Control Models:
• RBAC (Role-Based): Role ke basis par permissions
• DAC (Discretionary): Owner decide karta hai
• MAC (Mandatory): System decide karta hai (Military)
Principle of Least Privilege: Sirf utni permission do jitni zaroori hai.
3. Accounting (Hisaab/Logging)
Aapne andar aakar Kya kiya?
Ex: Logs check karna ki kisne file delete ki.
What to Log:
• Login attempts (success/failure)
• File access/modification
• System changes
• Network activity
Audit Trail: Complete history maintain karna—forensics ke liye zaroori hai.
AAA in Action: Real Examples
Example 1: Employee Database Access
Example 2: Cloud Storage Access
Example 3: Banking Transaction
AAA Failure Scenarios
Jab AAA fail hota hai, to kya hota hai:
- Authentication Failure: Weak password → Hacker guess kar leta hai → Account hack ho jata hai.
- Authorization Failure: User ko zyada permissions mil gayi → Normal user admin tasks kar sakta hai → Privilege escalation.
- Accounting Failure: Logs nahi hain → Attack hone ke baad pata nahi chalta ki kya hua → Forensics impossible.
💻 Tech Corner: Hashing vs Encryption - Complete Guide
Beginners aksar in dono ko same samajhte hain. Aaiye code se samajhte hain.
1. Encryption (Taala-Chabi)
Isme data ko lock kiya jata hai, aur chabi (Key) se wapas khola ja sakta hai. Ye Two-way process
hai.
Use: WhatsApp Messages, Bank Transfers, Email, Database encryption.
Types of Encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption: Same key encrypt aur decrypt dono ke liye (AES, DES). Fast hai, lekin key share karna mushkil.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Public key encrypt karti hai, Private key decrypt (RSA, ECC). Slow hai, lekin secure.
- Hybrid: Dono combine—symmetric key ko asymmetric se encrypt karke bhejte hain (HTTPS mein use hota hai).
2. Hashing (Juice Banana)
Ye One-way process hai. Jaise aap fruit se juice bana sakte hain, par juice se wapas fruit nahi
bana sakte.
Use: Storing Passwords, File Integrity Checks, Digital Signatures. (Facebook aapka password save nahi
karta, uska Hash save karta hai).
Common Hashing Algorithms:
- MD5: Old, weak—crack ho sakta hai. Ab use nahi karna chahiye.
- SHA-1: Weak—Google ne 2017 mein collision find kiya.
- SHA-256: Strong—Bitcoin aur modern systems mein use hota hai.
- bcrypt: Password hashing ke liye best—slow hai intentionally (brute force se bachata hai).
⚠️ Salt: Extra Security Layer
Agar do users ka same password hai, to hash bhi same hoga—ye problem hai. Salt ek random string hoti hai jo password ke saath add hoti hai.
Pepper: Even More Security
Pepper ek secret key hoti hai jo application level par hardcoded hoti hai—database mein nahi store hoti. Salt database mein store hoti hai, Pepper code mein.
Encryption vs Hashing: When to Use What?
Use Encryption When:
- Data ko wapas original form mein chahiye
- Messages, emails, files
- Database columns (credit cards)
- Network communication (HTTPS)
Use Hashing When:
- Data ko wapas original form mein nahi chahiye
- Passwords storage
- File integrity checks
- Digital signatures
- Blockchain transactions
Real-World Implementation Examples
Part 5: Defense in Depth - Multiple Security Layers
Ek hi security layer par depend karna dangerous hai. Defense in Depth ka matlab hai multiple layers lagana—agar ek fail ho, to doosri bachayegi.
Layer 1: Physical Security
Servers ko locked rooms mein rakho, CCTV, biometric access. Agar koi physically access kar le, to sab fail.
Layer 2: Network Security
Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), VPNs. Network level par attacks ko rokna.
Layer 3: Host Security
Antivirus, Host-based IDS, OS hardening. Individual devices ko secure karna.
Layer 4: Application Security
Code reviews, penetration testing, secure coding practices. Software level par security.
Layer 5: Data Security
Encryption at rest, encryption in transit, data classification. Data ko protect karna.
Layer 6: User Security
Training, awareness programs, phishing simulations. Users ko educate karna—weakest link hai.
1. Vendor access control weak tha
2. Network segmentation nahi thi
3. Payment system isolated nahi tha
Result: 40 million credit cards stolen. Defense in Depth nahi hone se ye hua.
Part 6: Real World Disasters - Case Studies
Theory samajh li, ab dekhte hain jab ye rules toot-te hain to kya hota hai.
1. WannaCry Ransomware (2017) - Availability Attack
Attack: Ek virus ne duniya bhar ke 200,000 computers ko lock kar diya. Hospitals, Banks, Railways
sab band. Screen par message aaya: "300$ do tabhi khulega".
Failure: Ye Availability ka failure tha. Data chori nahi hua, bas access
nahi ho raha tha.
How it Spread:
• EternalBlue exploit use kiya (NSA tool leak hua tha)
• Windows SMB protocol mein vulnerability thi
• Network par automatically spread hota gaya
Impact:
• UK NHS hospitals affected—surgeries cancel hue
• FedEx, Renault factories band
• Estimated loss: $4 billion globally
Lesson: Regular updates zaroori hain. Microsoft ne patch diya tha, lekin logon ne install nahi
kiya.
2. Twitter Bitcoin Hack (2020) - Integrity & Authentication Failure
Attack: Bill Gates, Elon Musk, Obama ke accounts se tweet hua "Mujhe 1000$ bhejo, main double
dunga".
Failure: Ye Integrity aur Authentication ka failure tha.
Hacker ne admin panel ka access lekar jhoot bola.
How it Happened:
• 17-year-old hacker ne Twitter employees ko call kiya (Vishing)
• Khud ko IT support bataya
• Employees se admin credentials le liye
• Internal tools access kar liye
Impact:
• 130 high-profile accounts compromised
• $120,000 Bitcoin collected (though most recovered)
• Twitter stock price drop hua
Lesson: Social Engineering se bhi bade systems hack ho sakte hain. MFA aur employee training
zaroori hai.
3. Equifax Breach (2017) - Confidentiality Failure
Attack: 147 million Americans ka personal data leak—SSN, credit card numbers, addresses.
Failure: Confidentiality ka massive failure.
Root Cause:
• Apache Struts framework mein vulnerability thi
• Patch available tha, lekin install nahi kiya
• Attackers ne 76 days tak access rakha
Impact:
• $700 million settlement
• CEO ne resignation di
• Millions ko identity theft ka risk
Lesson: Patch management critical hai. Vulnerability management process zaroori hai.
4. SolarWinds Attack (2020) - Supply Chain Attack
Attack: Hackers ne SolarWinds software update mein malware inject kar diya. 18,000 companies
affected.
Failure: Supply chain compromise—trusted vendor se malware aaya.
How it Worked:
• SolarWinds Orion software update mein backdoor
• Companies ne update install kiya—malware automatically install ho gaya
• Attackers ko network access mil gaya
Impact:
• US Government agencies affected (Treasury, Commerce)
• Microsoft, FireEye jaise companies affected
• Estimated cost: $100+ billion
Lesson: Third-party vendors ko bhi verify karna zaroori hai. Supply chain security important hai.
5. NotPetya Attack (2017) - Destructive Malware
Attack: Ransomware jaisa dikhta tha, lekin actually data destroy karne wala malware tha. Ukraine
mein start hua, lekin globally spread ho gaya.
Failure: Multiple failures—weak security, supply chain compromise, lack of segmentation.
How it Spread:
• Ukrainian accounting software update mein malware
• EternalBlue exploit use kiya (same as WannaCry)
• Network par automatically spread—ransomware jaisa dikha, lekin data permanently delete kar diya
Impact:
• Maersk (shipping company) - 49,000 computers affected, $300M loss
• FedEx - $400M loss
• Merck (pharma) - $870M loss
• Total global damage: $10+ billion
Lesson: Network segmentation zaroori hai—ek system compromise hone par sab affected na ho. Also,
backups verify karo—NotPetya ne backups bhi corrupt kar diye the.
6. Colonial Pipeline Ransomware (2021) - Critical Infrastructure
Attack: US ke largest fuel pipeline ko ransomware attack—5 days tak band raha.
Failure: Weak password, no MFA, VPN access compromised.
How it Happened:
• Employee ka compromised password (probably reused, leaked in breach)
• VPN access mil gaya—no MFA required
• Ransomware deploy kiya—systems lock ho gaye
• Company ne $4.4 million ransom pay kiya (though FBI recovered most)
Impact:
• 5,500 miles pipeline band—US East Coast fuel shortage
• Gas prices spike huye
• National emergency declared
• $4.4M ransom paid (DarkSide group)
Lesson: Critical infrastructure ko extra secure rakho. MFA mandatory hona chahiye. Password reuse
dangerous hai—one breach se multiple systems compromise ho sakte hain.
7. Log4j Vulnerability (2021) - Open Source Risk
Attack: Apache Log4j library mein critical vulnerability—millions of applications affected.
Failure: Open source dependency management, lack of visibility into dependencies.
What was Log4j?
• Java logging library—hundreds of millions of applications use karte hain
• Remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2021-44228)
• Attackers could execute code remotely—just by sending special text in logs
Impact:
• Apple iCloud, Steam, Minecraft affected
• Government systems affected globally
• Millions of servers vulnerable
• Patch quickly released, but many systems still unpatched
Lesson: Open source dependencies ko track karo. Dependency scanning tools use karo. Updates
regularly install karo. "It's just a logging library" soch kar ignore mat karo—even small libraries critical ho
sakti hain.
1. Initial Access: Weak password, phishing, unpatched vulnerability
2. Lateral Movement: Network par spread—more systems compromise
3. Impact: Data theft, system lock, or destruction
Defense strategy: Har step par detection aur prevention—Defense in Depth.
Part 7: Common Security Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Beginners aur companies dono ye galtiyan karte hain. Inhe avoid karke aap 80% attacks se bach sakte hain.
❌ Mistake 1: Weak Passwords
Problem: "password123", "admin", "123456" jaise passwords.
Solution: Strong passwords (12+ characters, mix of letters, numbers, symbols), Password
Manager use karo.
Stat: 81% breaches weak passwords se hote hain.
❌ Mistake 2: No Updates
Problem: System updates ignore karna.
Solution: Automatic updates enable karo, regular patch management.
Stat: 60% breaches unpatched vulnerabilities se hote hain.
❌ Mistake 3: No Backup
Problem: Data backup nahi karna.
Solution: 3-2-1 Rule: 3 copies, 2 different media, 1 offsite.
Stat: 93% companies jo 7 days backup nahi karte, business band kar dete hain.
❌ Mistake 4: No MFA
Problem: Sirf password par depend karna.
Solution: Multi-Factor Authentication enable karo—password + OTP/App.
Stat: MFA 99.9% attacks ko prevent karta hai.
❌ Mistake 5: Clicking Suspicious Links
Problem: Phishing emails par click karna.
Solution: Hover karke URL check karo, sender verify karo, suspicious links avoid karo.
Stat: 91% attacks phishing se start hote hain.
❌ Mistake 6: Public WiFi
Problem: Public WiFi par sensitive work karna.
Solution: VPN use karo, sensitive data avoid karo, HTTPS sites use karo.
Stat: Public WiFi par 40% traffic unencrypted hota hai.
Part 8: Career Paths in Cyber Security
Cyber Security mein career options bahut hain. Aap apni interest ke basis par choose kar sakte hain.
1. Ethical Hacker / Penetration Tester
Role: Systems ko hack karke weaknesses find karna (with permission).
Skills: Kali Linux, Metasploit, Nmap, Programming (Python, Bash).
Salary: ₹6-15 LPA (India), $70k-120k (US).
Certifications: CEH, OSCP, GPEN.
2. Security Analyst
Role: Threats detect karna, incidents investigate karna.
Skills: SIEM tools, Log analysis, Threat intelligence.
Salary: ₹4-10 LPA (India), $60k-100k (US).
Certifications: Security+, GSEC, CySA+.
3. Security Architect
Role: Security systems design karna.
Skills: Network security, Cloud security, Architecture design.
Salary: ₹15-30 LPA (India), $120k-180k (US).
Certifications: CISSP, CISM, SABSA.
4. Incident Responder
Role: Attacks hone par response karna, damage control.
Skills: Forensics, Malware analysis, Crisis management.
Salary: ₹8-18 LPA (India), $80k-130k (US).
Certifications: GCIH, GCFA, CHFI.
5. Security Consultant
Role: Companies ko security advice dena.
Skills: Risk assessment, Compliance, Communication.
Salary: ₹10-25 LPA (India), $90k-150k (US).
Certifications: CISSP, CISM, ISO 27001.
6. Bug Bounty Hunter
Role: Companies ke systems mein bugs find karke paise kamana.
Skills: Web app security, Mobile security, Creativity.
Salary: Variable—$0 to $1M+ (depends on bugs found).
Platforms: HackerOne, Bugcrowd, Synack.
Learning Path for Beginners - Complete Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-3)
Phase 2: Security Fundamentals (Months 4-6)
Phase 3: Hands-on Practice (Months 7-12)
Phase 4: Specialization (Year 2+)
✅ Consistency > Intensity: Har din 1 hour practice, 7 hours ek din se better hai
✅ Join Communities: Reddit r/netsec, Discord servers, Twitter security community
✅ Read Security News: Krebs on Security, The Hacker News, Bleeping Computer
✅ Practice Daily: Even 30 minutes TryHackMe room solve karo
✅ Don't Compare: Har kisi ka journey different hai—focus on your progress
Part 9: Security Frameworks & Standards
Real-world mein, companies frameworks follow karti hain—structured approach ke liye. Ye frameworks best practices define karte hain.
ISO 27001
What: International standard for Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Key Components:
• Risk assessment process
• Security controls (114 controls)
• Continuous improvement
Who Uses: Large enterprises, government agencies
Certification: Companies can get ISO 27001 certified
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
What: US National Institute of Standards framework—5 core functions.
5 Functions:
1. Identify (assets, risks)
2. Protect (safeguards)
3. Detect (monitoring)
4. Respond (incident handling)
5. Recover (restoration)
Who Uses: US government, many US companies
OWASP Top 10
What: Top 10 most critical web application security risks.
2021 List:
1. Broken Access Control
2. Cryptographic Failures
3. Injection (SQL, XSS)
4. Insecure Design
5. Security Misconfiguration
...and 5 more
Who Uses: Web developers, security testers
PCI DSS
What: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
Requirements:
• Secure network (firewalls)
• Protect cardholder data (encryption)
• Vulnerability management
• Access control
• Monitoring & testing
Who Uses: Companies handling credit card data
GDPR
What: General Data Protection Regulation (EU law).
Key Requirements:
• User consent for data collection
• Right to access/delete data
• Data breach notification (72 hours)
• Privacy by design
Who Uses: Any company handling EU citizen data
Penalty: Up to 4% annual revenue or €20M
CIS Controls
What: Center for Internet Security—20 critical security controls.
Examples:
• Inventory of authorized devices
• Secure configurations
• Continuous vulnerability assessment
• Controlled use of admin privileges
Who Uses: Organizations wanting practical, prioritized controls
Why Frameworks Matter
Frameworks provide:
- Structure: Chaotic approach se bachata hai—systematic way
- Compliance: Legal/regulatory requirements meet karne ke liye
- Best Practices: Industry-proven methods
- Communication: Common language—sabko pata hai kya expect karna hai
- Continuous Improvement: Regular assessment aur updates
Part 10: Emerging Threats & Future of Cyber Security
Cyber Security field constantly evolve hoti hai. Naye threats aate rahte hain. Aaiye dekhte hain future mein kya challenges hain:
1. AI-Powered Attacks
Threat: Attackers AI use kar rahe hain sophisticated attacks ke liye.
Examples:
• Deepfakes: Fake videos/audio—CEO ki awaaz mein call karke fraud
• AI-Generated Phishing: ChatGPT se perfect grammar wale phishing emails
• Automated Attacks: AI bots jo vulnerabilities find karte hain automatically
• Evasion: Malware jo AI use karke detection se bachta hai
Defense: AI-powered security tools—threat detection, anomaly detection
2. Quantum Computing Threat
Threat: Quantum computers current encryption ko break kar sakte hain.
Impact:
• RSA encryption (used in HTTPS, banking) break ho sakta hai
• Current passwords, encrypted data vulnerable ho jayega
• Timeline: 10-20 years (but preparation abhi se chahiye)
Defense: Post-quantum cryptography—quantum-resistant algorithms develop ho rahe hain
3. IoT Security Crisis
Threat: Billions of IoT devices—cameras, smart TVs, routers—weak security.
Problems:
• Default passwords (admin/admin)
• No security updates
• Weak encryption
• Botnet attacks (Mirai botnet ne 2016 mein major DDoS attack kiya)
Defense: Network segmentation, device authentication, regular updates
4. Supply Chain Attacks
Threat: Attackers vendors/third-party software ko target karte hain (SolarWinds jaisa).
Why Increasing:
• Companies third-party software use karti hain
• One compromise se multiple companies affected
• Hard to detect—trusted source se aata hai
Defense: Vendor security audits, software composition analysis, least privilege
5. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Threat: Ransomware gangs ne "business model" bana liya—anyone ransomware use kar sakta hai.
How it Works:
• Ransomware groups provide platform/tools
• Affiliates attacks run karte hain
• Profit share (70-30, 80-20)
• Lower barrier to entry—less skilled attackers bhi kar sakte hain
Defense: Same as ransomware—backups, segmentation, training
• 2025-2030: AI vs AI battles—attackers aur defenders dono AI use karenge
• 2030+: Quantum computing mainstream—post-quantum crypto transition
• Ongoing: Skills shortage—demand zyada hai, supply kam hai
• Opportunity: Cyber security jobs 35% growth rate (2022-2032)
Conclusion: The Cyber Security Mindset
Cyber Security koi software nahi hai jise aap install kar lein. Ye ek Mindset hai.
Ek Hacker hamesha 100 darwaze check karega. Agar 99 band hain aur 1 khula hai, to wo jeet gaya.
Ek Security Expert ko wo 100 ke 100 darwaze band rakhne hote hain. Hamara kaam mushkil hai, lekin zaroori hai.
Remember:
✅ Perfect security impossible hai—goal hai risk ko acceptable level tak reduce karna
✅ Security ek process hai, ek product nahi—continuous improvement chahiye
✅ Defense in Depth—ek layer fail ho, to doosri bachayegi
✅ Human factor sabse weak link hai—training aur awareness zaroori hai
✅ Learning never stops—field constantly evolve hoti hai, adapt karna padta hai
✅ CIA Triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability) har security system ka foundation hai
✅ AAA Model (Authentication, Authorization, Accounting) access control karta hai
✅ Defense in Depth—multiple security layers zaroori hain
✅ Encryption vs Hashing—dono different hain, dono zaroori hain
✅ Regular updates, strong passwords, MFA—basics follow karo
✅ Learning never stops—cybersecurity constantly evolve hoti hai
Essential Tools & Resources
Must-Have Tools for Beginners
Kali Linux
What: Penetration testing distribution—pre-installed security tools.
Tools Included: Nmap, Metasploit, Burp Suite, Wireshark, John the Ripper
Download: kali.org
Use: VirtualBox mein install karo, practice ke liye
VirtualBox/VMware
What: Virtualization software—safe environment banane ke liye.
Why: Real system ko risk mein daale bina practice kar sakte hain
Download: virtualbox.org (free)
Use: Kali Linux aur vulnerable VMs run karne ke liye
Burp Suite Community
What: Web application security testing tool.
Features: Proxy, scanner, repeater, intruder
Download: portswigger.net (free community edition)
Use: Web apps test karne ke liye
Wireshark
What: Network protocol analyzer—packet capture aur analysis.
Use: Network traffic analyze karna, attacks understand karna
Download: wireshark.org (free)
Learning: Network protocols samajhne ke liye best
Learning Platforms
- TryHackMe: Beginner-friendly, guided paths, free tier available (tryhackme.com)
- HackTheBox: More challenging, real-world scenarios, free tier (hackthebox.com)
- PortSwigger Web Security Academy: Free web app security training (portswigger.net/web-security)
- OverTheWire: Command line challenges, free (overthewire.org)
- PicoCTF: Annual CTF competition, free practice (picoctf.org)
- Cybrary: Free security courses (cybrary.it)
- Professor Messer: Free Security+ training videos (professormesser.com)
Communities & Forums
- Reddit: r/netsec, r/cybersecurity, r/AskNetsec, r/hacking
- Discord: TryHackMe Discord, HackTheBox Discord, InfoSec Community
- Twitter: Follow #InfoSec, #Cybersecurity hashtags, security researchers
- LinkedIn: Cyber security groups, professionals se connect
- GitHub: Security tools, scripts, learning resources
News & Blogs
- Krebs on Security: In-depth security investigations (krebsonsecurity.com)
- The Hacker News: Daily security news (thehackernews.com)
- Bleeping Computer: Security news, malware analysis (bleepingcomputer.com)
- Dark Reading: Enterprise security news (darkreading.com)
- OWASP: Web security resources (owasp.org)
Next Steps - Your Action Plan
Ab aapne fundamentals seekh liye hain. Aage kya karna hai? Ek structured plan:
💡 Pro Tips for Success
1. Consistency Over Intensity: Har din 1 hour practice, 7 hours ek din se zyada better hai.
Small daily progress compound hota hai.
2. Hands-on Practice: Sirf padhne se kaam nahi chalega. Tools use karo, labs solve karo,
mistakes se seekho.
3. Build a Lab: Apna virtual lab setup karo—Kali Linux, vulnerable VMs. Experiment karo, break
karo, fix karo.
4. Document Everything: Jo bhi seekha, notes banao. Blog likho, GitHub par scripts share karo.
Portfolio banata hai.
5. Join Communities: Reddit, Discord, Twitter—experts se connect karo, questions pucho,
discussions mein participate karo.
6. Stay Updated: Security field fast-changing hai. News follow karo, new attacks study karo,
tools explore karo.
7. Don't Compare: Har kisi ka journey different hai. Focus on your progress, not others'.
Remember: Har expert ek din beginner tha. Start karo, consistent raho, aur kabhi ruko mat.
Cyber Security ek marathon hai, sprint nahi.
📚 Recommended Reading
Books for Beginners:
• "The Web Application Hacker's Handbook" - Web security ke liye
• "Metasploit: The Penetration Tester's Guide" - Penetration testing
• "Applied Cryptography" by Bruce Schneier - Encryption deep dive
• "The Art of Exploitation" - Low-level security concepts
Free Resources:
• OWASP Top 10 documentation (owasp.org)
• NIST Cybersecurity Framework (nist.gov)
• SANS Reading Room (sans.org/reading-room) - Free security papers
• CVE Database (cve.mitre.org) - Known vulnerabilities
📝 Final Assessment - Test Your Knowledge
Q1: Facebook aapke password ko Database me kaise store karta hai?
Q2: Agar kisi ne Website par dher saara traffic bhej kar use Down kar diya, to CIA ka kaunsa pillar toota?
Q3: "Vulnerability" ka sahi matlab kya hai?
Q4: AAA Model mein "Authorization" ka matlab kya hai?
Q5: Encryption aur Hashing mein kya difference hai?
Q6: Defense in Depth ka matlab kya hai?
Q7: WannaCry ransomware attack kis CIA pillar ko target kiya?
Q8: Salt ka use password hashing mein kyun kiya jata hai?
Q9: Zero-Day Vulnerability kya hoti hai?
Q10: Risk ka formula kya hai?
📊 Score Interpretation
8-10 Correct: Excellent! Aapne fundamentals achhe se samajh liye hain. Aage advanced topics par
focus karo.
5-7 Correct: Good! Basics clear hain, lekin kuch concepts par aur practice chahiye. Dobara
padho aur examples practice karo.
0-4 Correct: Don't worry! Ye normal hai first time mein. Blog dobara padho, examples samjho,
aur phir se try karo.